what is saffron used for
- What is saffron?
- What is saffron stigma?
- What are the benefits of saffron?
- What are the side effects of saffron?
- Everything about saffron cultivation
- What are the uses of saffron?
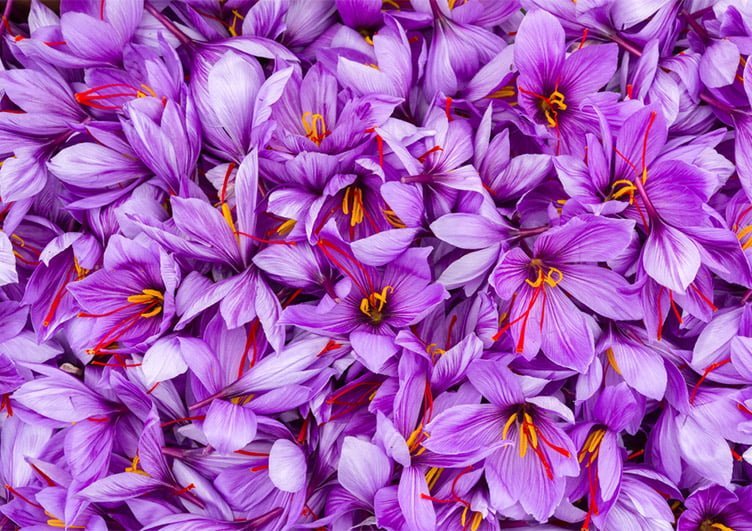
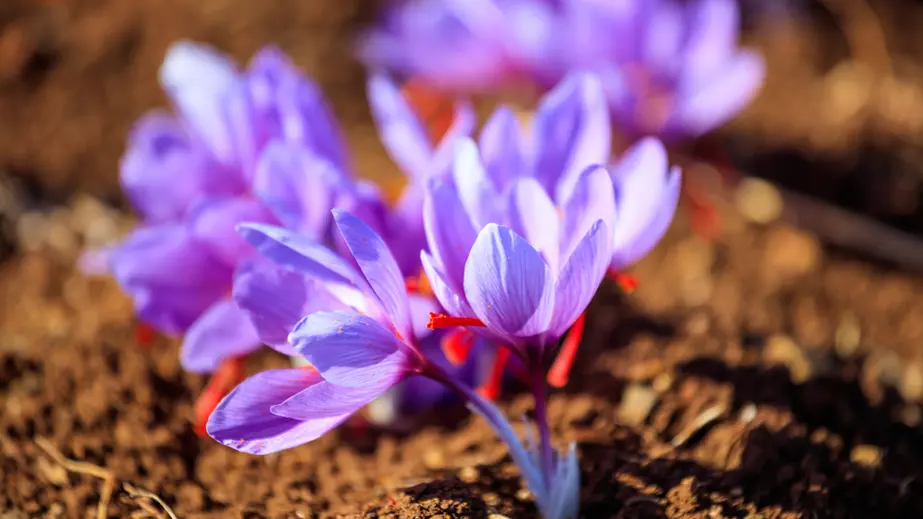
- Saffron Flower:
- Sources to ensure authenticity
- The Best Types of Saffron
- History of saffron:
WHAT IS SAFFRON?
Saffron is widely regarded as one of the most precious spices globally, derived from the blossoms of the saffron plant.
Saffron plants thrive in warm and dry regions. Iran, for instance, boasts of such ideal climatic conditions, including warm and dry weather, well-drained soil, high altitude from sea level, and abundant sunlight. As a result, Iran is the world’s leading producer of saffron, accounting for over 90% of its global production.
In addition to Iran, countries such as Spain, Greece, Italy, various Middle Eastern countries, India, China, and Afghanistan are also recognized as saffron-producing nations worldwide.
Saffron finds applications in diverse industries, including the food sector, cosmetics and perfumery, pharmaceuticals, traditional medicine, the textile industry, and handicrafts. Saffron is widely used in the food industry because of its exceptional color, aroma, and taste, as well as its mineral content and array of vitamins.
Due to the unique conditions required for cultivation, the manual labor involved in separating saffron threads from the flowers, the costly production and packaging processes, as well as the time-intensive harvesting process, saffron has gained recognition as the world’s most expensive and highly prized spice.

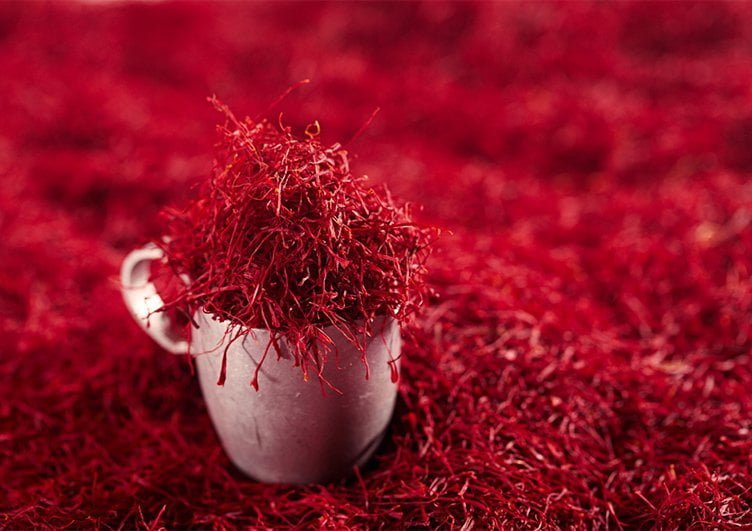
What is saffron stigma?
The saffron stigma, commonly known as saffron threads, is a component of the saffron flower. It is a long and slender filament that extends from the flower and reaches down to the root of the plant. The stigma of the saffron plant is a deep red or crimson hue, and it holds great significance as it is primarily used for extracting essence and obtaining the golden color. The size of the saffron stigma can vary depending on environmental conditions, typically ranging from 3 to 5 centimeters. It is important to note that the saffron stigma is considered the most valuable component of this plant.
The saffron stigma is highly regarded for its significant value and expensive nature. It consists of several components, including the “Khamah” (root), “Pushal” (base), “Negin” (filament), “Super Negin,” and “Sargol” (top).
KHAMAH (ROOT):
Khamah, which is a component located at the base of the saffron stigma, accounts for approximately 40-50 percent of the entire stigma. The Khamah of saffron is known for its anti-inflammatory, anticancer, and antioxidant properties.
PUSHAL (BASE):
Pushal refers to the lower portion of the saffron stigma, which is covered with a white or yellowish-white color. Its main purpose is to safeguard the filaments and prevent them from becoming fragile. Pushal is known for its anti-inflammatory and soothing properties. It has been used in traditional medicine to treat respiratory infections such as the common cold and sinusitis.
NEGIN AND SUPER NEGIN:
Negin and Super Negin are saffron stigmas with an orange to reddish color. They contain components such as Crocin, Picrocrocin, and Safranin. These constituents of saffron have properties that include being anticancer, anti-inflammatory, and anxiolytic.
SARGOL (TOP):
Sargol is composed of the highest portion of the saffron stigma, which is characterized by a deep red to reddish-brown color. Sargol exhibits various properties, including anticancer, anxiolytic, antidepressant, and anti-inflammatory effects. The use of saffron has been acknowledged as an effective approach in alleviating menstrual pain. Furthermore, Sargol saffron has the highest concentration of its distinct color, making it a crucial factor in determining the overall quality of saffron.

After the annual saffron harvest, which takes place during the autumn season, the stigmas and petals of saffron are meticulously separated from each other. There are two different approaches to drying saffron stigmas: traditional drying, which involves placing them on a heater, or utilizing a drying machine. It takes around 150,000 to 200,000 saffron flowers in order to yield one kilogram of saffron stigmas.
The saffron stigma consists of a variety of chemical compounds, including crocin, picrocrocin, safranin, carotenoids, and various essences. These components are responsible for the numerous benefits associated with saffron. These compounds exhibit various beneficial properties, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antimicrobial, anticancer, and anxiolytic effects. Moreover, the saffron stigma is rich in essential minerals such as potassium, calcium, copper, sodium, iron, and magnesium. These minerals play a crucial role in maintaining optimal health. Moreover, due to its vibrant red color, the saffron stigma is used as a natural dye in various industries including food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics. As a result, the saffron stigma holds great value within the saffron flower and is considered to be the most expensive spice in existence.

What are the benefits of saffron?
Saffron possesses numerous properties and is a rich source of various vitamins as well as a wide range of minerals, including potassium, calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, sodium, and zinc. Furthermore, saffron is abundant in vitamins that contribute to maintaining overall health.
Some of the important vitamins found in saffron are:
- Vitamin C:It functions as an antioxidant and plays a crucial role in preserving skin health, as well as supporting the immune system.
- Vitamin B6: It has been found to have benefits in amino acid metabolism, protein synthesis, and the production of essential hormones.
- Vitamin A:It plays a crucial role in maintaining eye and skin health, while also functioning as an antioxidant.
- Vitamin K:Maintaining bone health and the integrity of blood vessels is crucial for overall physical well-being.
DUE TO THE NUMEROUS BENEFITS OF SAFFRON, IT IS EXTENSIVELY USED IN THE PRODUCTION OF MEDICINES. SOME OF THE MEDICINAL PROPERTIES OF SAFFRON THAT LEAD TO ITS USE IN THE PHARMACEUTICAL INDUSTRY ARE AS FOLLOWS:
- Antidepressant properties:Saffron compounds, namely crocin, picrocrocin, and safranin, possess antidepressant properties and have demonstrated efficacy in alleviating symptoms of depression and anxiety. Multiple research studies have provided evidence that the intake of saffron has the ability to increase serotonin levels in the brain. This, in turn, leads to improvements in mood and a reduction in symptoms associated with depression.
- Anti-inflammatory properties:Saffron compounds, such as crocin and safranin, possess anti-inflammatory properties and are utilized in the development of pharmaceuticals targeting anti-inflammatory effects.
- Anticancer properties:Several studies have shown that compounds found in saffron may have potential benefits in preventing and treating certain types of cancer. One notable example is crocin, a compound present in saffron, which has shown promise in preventing prostate and breast cancer.
- Treatment of cardiovascular diseases:Studies have indicated that compounds found in saffron, such as crocin and safranal, have been proven to effectively lower blood pressure, reduce levels of blood cholesterol, and enhance heart function.
However, in order to fully utilize the benefits of saffron and its use as an herbal remedy, it is highly recommended to seek guidance from a physician or nutrition specialist. This will help mitigate any potential adverse effects.

What are the side effects of saffron?
The use of saffron offers numerous advantages, and ensuring proper quantities and following recommended guidelines ensures both safety and benefits. Nevertheless, it is important to note that excessive or improper use of saffron can potentially have adverse effects on one’s health. Some disadvantages associated with the misuse of saffron include:
INCREASED RISK OF BLEEDING:
Saffron is known to contain various compounds, including crocin, picrocrocin, and other specific elements. These components may potentially be linked to mechanisms involving platelets and bleeding. Therefore, excessive consumption of saffron without proper medical supervision may increase the risk of bleeding, especially for individuals with blood disorders or a history of excessive bleeding. Furthermore, it is important to note that saffron may interact with blood-thinning medications. Therefore, using saffron in combination with these medications could potentially increase the risk of bleeding.
MISCARRIAGE:
Due to the presence of numerous chemical compounds and potential adverse effects, it is strongly advised to completely avoid consuming saffron during pregnancy. Specifically, crocetin, one of the compounds found in saffron, may excessively stimulate the uterus when consumed in large quantities. Crocetin has the ability to increase estrogen levels in the body, which can stimulate the uterus. As a result, this may cause strong and involuntary contractions that can negatively impact fertility and potentially lead to miscarriage.
NERVOUS SYSTEM STIMULATION:
Excessive consumption of saffron has the potential to stimulate the nervous system and cause various side effects. These may include increased blood pressure, sleep disturbances, anxiety, sweating, headaches, and even cardiac insufficiency. Moreover, the consumption of excessive amounts of saffron can lead to adverse health effects, such as allergies and potentially life-threatening anaphylactic shock. When saffron is combined with medications that affect the central nervous system, such as sedatives, it has the potential to amplify the adverse effects of these drugs in certain cases. Therefore, it is recommended to seek medical advice before using saffron if you are currently taking any prescribed medication.
INCREASED BLOOD PRESSURE:
The excessive consumption of saffron has the potential to elevate blood pressure due to the presence of active compounds like crocin. These compounds can cause tension in the blood vessels, leading to an increase in blood pressure. The tension experienced causes an increase in the thickness of blood vessel walls, leading to elevated blood pressure. Additionally, excessive consumption of saffron can potentially result in higher sodium levels in the body, which can also contribute to elevated blood pressure levels.
ALLERGIES AND SENSITIVITIES:
The reason for this is the presence of certain chemical compounds in saffron that may not be compatible with the body’s immune system, thus causing allergies and sensitivities. While saffron allergies are uncommon, they can still affect certain individuals. Symptoms of saffron allergies and sensitivities may include facial swelling, itching, redness, and swelling. Individuals with saffron allergies may experience additional symptoms, such as headaches, difficulty breathing, fever, and gastrointestinal problems like diarrhea and nausea.
GASTROINTESTINAL SIDE EFFECTS:
The consumption of saffron may lead to adverse effects such as indigestion, bloating, heartburn, diarrhea, and nausea. These side effects are primarily caused by excessive intake of saffron. The excessive consumption of saffron can potentially stimulate the digestive system and lead to an increase in stomach acid secretion, resulting in indigestion and abdominal discomfort.

Everything about saffron cultivation
The Saffron flower is a perennial plant with very narrow leaves that is accustomed to warm and dry climates. The following conditions must be met for saffron cultivation:
- Saffron grows in regions with a warm and dry climate such as Iran, Afghanistan, Spain, countries in the Eastern Mediterranean, and Northwestern Iran.
- The soil should have high drainage capacity, contain suitable nutrients, and have a pH between 6 to 8.5.
- The Saffron plant requires a minimum of 8 hours of sunlight per day.
- Saffron requires less water compared to other plants. For example, when saffron flowers are growing, approximately 15 to 20 liters of water should be poured per square meter of land.
- The suitable temperature for saffron growth is between 17 to 35 degrees Celsius.
- It is better to use seeds from the previous season for saffron cultivation, and the planting time is in the spring season.
By observing the above conditions, saffron flowers can be successfully cultivated.
Iran, considering its climatic conditions and having a warm and dry climate, possesses more than 90% of the world’s saffron production. Additionally, countries such as Spain, Greece, Italy, Middle Eastern countries, India, China, and Afghanistan are also among the saffron-producing countries.

What are the uses of saffron?
Saffron possesses a multitude of properties and finds applications in various fields. Due to its intense fragrance, flavor, and coloring capabilities, saffron serves as a versatile ingredient in a wide range of industries. Here are examples of industries that leverage the use of saffron to produce a diverse range of products:
- FOOD INDUSTRY:
Saffron is widely used in the food industry as a spice. It serves as both a flavor enhancer and a coloring agent in numerous culinary preparations, desserts, and beverages. Saffron has multiple applications in the food industry, including its use in pastries, beverages, and the preparation of saffron oil. This oil, which is derived from saffron, serves as a key ingredient in specific dishes, beverages, and medicines.
Saffron holds significant value in the food industry due to its numerous advantageous characteristics. In addition to its applications in the culinary field, saffron is widely acknowledged for its medicinal properties as an herbal remedy.
- PHARMACEUTICAL INDUSTRY:
Saffron is used as a key ingredient in the production of certain medications in the pharmaceutical industry, due to its beneficial medicinal properties. As an example, saffron is used in the production of antidepressants, painkillers, anti-inflammatory drugs, and cardiac medications. Saffron is known for its antispasmodic and anti-inflammatory properties, which make it a potential treatment option for certain health conditions. One example of its usefulness is in addressing digestive issues such as stomach pain, diarrhea, and constipation, thanks to its natural antispasmodic effects. Moreover, saffron possesses anti-inflammatory properties that can effectively alleviate inflammation associated with cardiovascular diseases, rheumatic conditions, muscular discomfort, and joint pain.
- COSMETICS AND PERSONAL CARE INDUSTRY:
The cosmetic industry benefits from the application of saffron due to its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. One example of saffron utilization in this industry can be seen in the manufacturing of anti-aging creams and products that are designed to reduce wrinkles. The anti-aging and anti-inflammatory properties of saffron make it suitable for use in the production of acne treatments, lotions, facial masks, soaps, and shampoos. Moreover, saffron, which is a natural coloring agent with excellent color intensity, is widely used in the cosmetic industry. It is commonly found in various products such as nail polish, lipsticks, blushes, and facial makeup.
- TEXTILE INDUSTRY:
In addition to its contributions to cooking and medicine, saffron also plays a significant role in the textile industry as a natural dye. One particular application of saffron is in the creation of natural dyes for coloring fabrics and garments. The natural color of saffron, along with its antibacterial and antifungal properties, reduces the need for chemical substances and promotes environmental preservation. Furthermore, natural saffron dyes are widely acknowledged to surpass synthetic dyes in terms of both quality and color stability. As a result, saffron is extensively used in various applications within the textile industry, including the production of natural dyes and insect repellents. Saffron is also used in the handicraft industries for tasks such as fabric dyeing, creating handwoven textiles, and leather dyeing, among other applications.
- PERFUME INDUSTRY:
Saffron is also used in the perfume industry. Perfumers utilize saffron flowers to create fragrances and essences. The perfumes crafted with saffron essences are characterized by warm and bittersweet scents, often used in men’s fragrances.

Saffron Flower
Saffron is an herbaceous plant that belongs to the sunflower family (Crocus sativus). It thrives in warm and dry regions with high altitudes. The plant requires well-textured soil that provides excellent drainage capacity. The saffron flower has a size ranging from two to three centimeters and features six distinct vivid purple petals. It is composed of three floral components: a central column, lower stigmas, and a crimson spot. The portion of saffron that is used consists of the extract derived from the upper three petals, which is manually separated from the flowers. This extract, commonly known as saffron, holds significant economic value.
The saffron plant is widely regarded as the most valuable spice globally, thanks to its distinct fragrance, flavor, exceptional coloring properties, and numerous benefits.

Sources to ensure authenticity
The Saffron Flower is known for its substantial nutritional value and consequently holds a position among the costliest spices. However, the market is plagued with the issue of counterfeit and impure saffron due to inadequate supervision and standards. Therefore, it is essential to exercise extreme caution when contemplating the purchase of saffron.
Using scientific techniques and conducting precise testing is the most reliable approach for determining the authenticity and purity of saffron. Nevertheless, there are certain key distinctions between genuine and counterfeit saffron that can help in avoiding the purchase of fake saffron. Several factors to consider when differentiating between authentic and fake saffron are as follows:
- Taking into consideration the cost of saffron.
- When considering the cost of saffron.
- Observing the disparity in the speed at which color is infused.
- Analyzing the visual attributes of saffron.
- It is advisable to carefully inspect the product labels and official quality control marks before making a purchase.
To ensure the quality of your purchase, it is advisable to buy from reputable stores. Using authentic and genuine saffron is crucial for maintaining optimal health.

The Best Types of Saffron
Saffron is widely regarded as one of the most exclusive and valuable spices globally, often referred to as “red gold.” While saffron production occurs in various regions worldwide, certain varieties are distinguished by their superior quality and unique traits.
SOME OF THE BEST TYPES OF SAFFRONS INCLUDE:
- Iranian Saffron, also known as Saffron Coupe, is highly esteemed for its deep red hue, robust flavor, and delightful fragrance.
- La Mancha Saffron is renowned for its deep saffron hue, exceptional quality, and robust flavor, positioning it as one of the most superior saffron varieties globally.
- Kashmiri saffron garners significant attention due to its deep red hue, delightful flavor, and exceptional fragrance.
Each of these saffron varieties possesses distinctive characteristics and properties. Among them, Iranian Saffron is widely celebrated as one of the most exquisite and renowned types. It is notably distinguished by its exceptionally high quality, deep red color, robust flavor, and exceptional aroma. Each of these saffron varieties possesses distinctive characteristics and properties. Among them, Iranian Saffron is widely celebrated as one of the most exquisite and renowned types. It is notably distinguished by its exceptionally high quality, deep red color, robust flavor, and exceptional aroma.
Iranian Saffron is widely acknowledged as the most renowned saffron globally due to several factors. These factors include its exceptional quality, significant historical importance, ideal cultivation conditions, slender threads (stigmas), distinctive flavor, and therapeutic attributes. Furthermore, Iran’s geographical location provides optimal conditions for cultivating and producing saffron of superior quality.
Furthermore, it is crucial to meticulously carry out each stage of saffron production, which includes cultivation, harvesting, drying, and packaging. This is essential to achieve the highest level of quality for the saffron product. NAVID SAFFRON Khorasan Razavi Company strictly adheres to international standards by implementing enhanced cultivation practices and abstaining from the use of chemical substances. After the harvest is complete, saffron threads undergo a drying process in sanitary conditions using drying machines. They are then carefully packaged and made available in the market after undergoing a thorough quality assessment.
HISTORY OF SAFFRON
The origins of saffron can be traced back thousands of years, with the Middle East being recognized as its primary source. Being one of the oldest spices in the world and possessing remarkable characteristics, saffron has been cultivated in various regions throughout history. Saffron is highly regarded by Iranians as one of their foremost agricultural commodities. The Khorasan region, due to its geographic position, is acknowledged as the primary center for saffron cultivation in Iran. It is important to note that Iran holds a leading position in saffron consumption, as it is responsible for producing over 90% of the global supply.